3D Point Cloud Technology Series (I) @0530- Dr. Junchao Yang
2021-07-07
1. The introduction
3D point clouds, which are mainly derived from 3D sensors, including various 3D scanners, Lidars, and RGB-D cameras. A 3D point cloud is a data set of points in a coordinate system. Points contain a wealth of information, including 3D coordinates X, Y, Z, color, classification values, strength values, time, and more. 3D point cloud can atomize the real world, and the real world can be restored through high-precision point cloud
1. The introduction
3D point clouds, which are mainly derived from 3D sensors, including various 3D scanners, Lidars, and RGB-D cameras. A 3D point cloud is a data set of points in a coordinate system. Points contain a wealth of information, including 3D coordinates X, Y, Z, color, classification values, strength values, time, and more. 3D point cloud can atomize the real world, and the real world can be restored through high-precision point cloud data. Point cloud representation, as a common representation format, retains the original geometric information in the three-dimensional space and does not need any discretization. As a result, it is the preferred representation for many scenarios understanding related applications, such as autonomous driving and robotics.
A 3D scanner is a scientific instrument used to detect and analyze the shape (geometry) and appearance data (such as color, surface albedo, etc.) of an object or environment in the real world. The collected data is often used to perform three-dimensional reconstruction calculations, creating digital models of real objects in a virtual world.
Lidar, or Ldar, is an optical remote-sensing technology that measures parameters such as the distance of a target by shining a beam of light, usually a pulsed laser. LiDAR is a kind of lidar, which is often used for 3D point cloud generation. Its working principle is to transmit the detection signal (laser beam) to the target, and then compare the received signal (target echo) reflected from the target with the transmitted signal. After proper processing, the relevant information of the target can be obtained, such as the target distance, azimuth, height, speed, attitude, and even the shape and other parameters.
Fig. 1 is a schematic diagram of 3D point cloud.
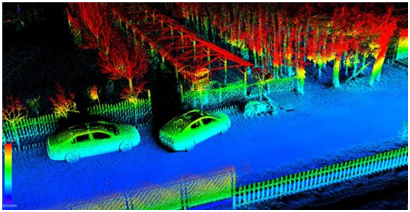
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of 3D point cloud
2. Data storage and algorithm library
2.1 Storage format
The main storage formats include: PTS, LAS, PCD,.xyz and.pcap.
The. PTS point cloud file format is the simplest point cloud format. It directly stores point cloud data in order of XYZ, which can be integral or floating point.
LAS is a laser radar data (LIDAR) storage format more complex than PTS and is intended to provide an open format standard that allows different hardware and software providers to output an interoperable unified format. Screenshot of point cloud in LAS format, where C: Class, F: Flight, T: Time, I: Intensity, R: Return, N: Number of Return, A: Intensity Scan Angle, RGB: Red Green Blue (RGB color value)
PCD storage format, the existing file structure due to its own composition does not support the introduction of n-dimensional point type mechanism by the PCL library processing some of the extensions, and PCD file format can be a good complement to this point. The PCD format has a file header that describes the overall information of the point cloud: the readable header that defines the number, the size, the dimension of the point cloud and the data type; A segment of data, which may be ASCII or binary. The data body part consists of the Cartesian coordinates of the points, with Spaces as delimiters in text mode.
.xyz A text format in which the first three digits represent the coordinates of a point and the next three digits represent the normal vector of the point, separated by Spaces.
PCAP is a common data stream format. The popular Velodyne lidar acquires data file format by default (manufacturer format). It is a binary file. There is a GlobalHeader, and then it is divided into several packets. Each Packet has a part containing headers and data.
2.2 Basic Algorithm
PCL (Point Cloud Library) supports cross-platform storage. Can be applied to calculation of limited resources and limited memory application scenarios, is a large open source cross-platform c + + programming, it implements the general algorithm of a large number of point cloud related and efficient data structure, realizes the point cloud related acquisition, filtering, segmentation, registration, retrieval, feature extraction, recognition and tracking, curved surface reconstruction and visualization operation, very convenient mobile client development.
The VCG library (Visualized and Computer Graphics Libary) is specially designed to deal with triangular grids. It is large and provides many advanced functions of handling grids, as well as a relatively small function of handling point clouds.
The CGAL (Computational Geometry Algorithms Library) is designed to provide convenient, efficient and reliable geometric Algorithms in the form of a C++ Library. It has implemented many Algorithms for dealing with point clouds and grids.
Open3D is an open source library that enables rapid development of 3D data processing software. Support for rapid development of software for processing 3D data. The Open3D front-end exposes a carefully selected set of data structures and algorithms in C++ and Python. The back end is highly optimized and set to parallelize. Open3D was developed from the start with very few, carefully considered dependencies. It can be set up on different platforms and can be compiled from source code with minimal effort. Code is clean, consistent in style, and maintained through clear code review mechanisms. Support on point cloud, grid, RGBD data.
2.3 Representation method of 3D point cloud
Method based on two-dimensional projection. The 3D point cloud data is projected onto the 2D image plane.
A method based on three dimensional voxels. The 2D projection of 3D point cloud reduces the difficulty of algorithm processing, but the 3D to 2D projection will inevitably bring the loss of geometric structure information, so it is very necessary to directly extract 3D features in some scenes. At the same time, the Voxelization of the point cloud is carried out to transform it into a grid with regular spatial arrangement, so that it can be directly applied to this representation.
The original point-based approach. Both the two-dimensional projection and the three-dimensional voxel need to transform the original point cloud to some extent, and the conversion will inevitably bring the loss of data information.
Graph based approach. In real life, there is a large amount of unstructured data, such as traffic network, social network, etc., and there are connections between nodes of these data, which can be expressed as graphs. The study of graph data is a hot topic in recent years. 3D point cloud data can be regarded as a kind of graph data, and many ideas of graph network can be used for reference in feature learning of point cloud data.
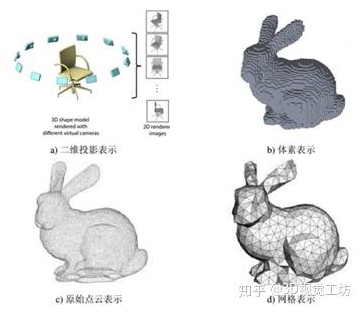
Fig. 2 3D point cloud representation
Different representations correspond to different treatments. The simple processing method is to project it into a two-dimensional image or transform it into a three-dimensional Voxel, so as to transform the disordered space points into regular data arrangement. It is also possible to use the original point as a representation without making any transformations. The advantage of this approach is to retain all the original information as much as possible. In addition, as a spatial disordered point set, point clouds can be regarded as graph data in the universal sense. There is another representation of point cloud, called Mesh, which can also be regarded as the points that build local connection relations, namely, graph. Point clouds are regarded as Graph data, which can be processed by Graph Convolution, a new technology in Graph field. It should be mentioned that there is no clear boundary between the original point representation and the graph representation (in fact, there is some difference between the original point cloud and the Mesh, but from the perspective of semantic understanding methods, this difference can be ignored for the time being and the Mesh can be regarded as an added connection).
3. The conclusion
3D point cloud has spatial coordinates, so it is widely used in surveying and mapping, construction, industry, automobile, game, criminal investigation and many other fields. Deep learning on 3D point clouds still faces several major challenges, such as the small size of the data set, the high dimension and the unstructured nature of 3D point clouds. At the same time, the classical processing method of 3D point cloud has certain reference significance for VR content processing and holographic video processing.
