google glass--Dr. Li Weina
2020-12-16
A brief introduction to Google Glass
Google Glass (Google Glass) is lighter than Microsoft (MicroSoft) Hololens. The latest Google Glass Enterprise Edition 2 is shown in Figure 1. It weighs only 46g, uses Android Oreo operating system, and is equipped with Qualcomm's XR1 processing. (This chip specially designed for mobile devices AR and VR uses a quad-core design, the highest frequency is 1.7GHz, and it supports up to 3GB of storage), has a 640×360 optical display module, and 3 beam-forming microphones (beam- forming microphones) (Beam forming is a technology that uses the phase difference between multiple sets of microphones to reduce the sound outside the target direction, not only can reduce environmental noise, but also improve the clarity of the target sound), multi-touch recognition gesture The directional touchpad is waterproof and dustproof, with battery life, and it costs $999.
From April 2013 to May 2014, Google started selling the Google Glass Explorer version for $1,500 (Figure 2), because it has too few applications, is expensive, and has a silent camera function. Give people concerns about privacy. After three years of silence, when people felt that Google Glass had failed, Google released the Google Glass Enterprise Edition in June 2017, which has faster Wi-Fi support, increased the camera to 8 million pixels, and added A red dot is added to warn of the function being filmed to protect privacy. This glasses is aimed at corporate users, and the focus is on liberating hands. Because corporate users require high productivity and efficiency, their demand for "freeing hands" is the strongest. For example, when workers pick up accessories, they don’t need to fill in the list at all. They can identify and record with a scan of the glasses, which is accurate and convenient; if they encounter problems that can’t be solved, they can connect directly with the engineer for remote guidance; when necessary , It can also record video, which is very convenient. It is said that Google has conducted an experiment, and it is 34% faster to work with Google Glass assistance when doing the same work than without assistance.

Figure 1. Google Glass Enterprise Edition 2 (Enterprise Edition 2)

Figure 2. Google Glass Explorer Edition (Explorer Edition)
Google's hardware director Rick Osterloh admitted that Google is still very interested in smart glasses (smartglass: Google glasses, hololens and other AR or VR glasses are smartglass), but if you want to make a breakthrough, you must wait for further technological development. Next, we will briefly introduce the structure diagram and components of Google Glasses based on Google's published patents.
1. Google Glass example 1
Google introduced a head-mounted electronic device in patent US 2013/0231273 A1 (as shown in Figure 3). Its frame includes a frame and lenses, a display element on the lens (as shown in Figure 3 454), and placement The arm frame 414 at the temple position (the arm frame 414 also includes elements such as 416, 450, 452, 470, 453, 472, 476). This example is shown in Figure 4 if worn on the user’s head. Figure 4 includes frames 430A and 430B, two lenses 418, nose pads 424, nose bridge part 420, arm frame 414 (including display 454, turning part 450, touch Type input 470). In addition to the camera, this patent only introduces one input device, namely touch input (as shown in 470 in Figure 4).
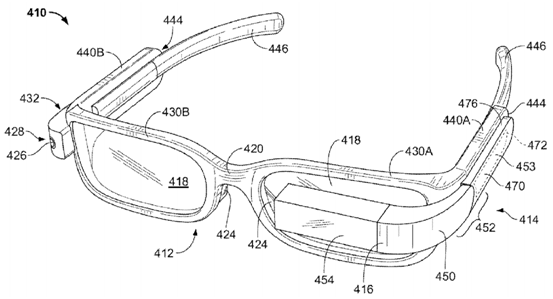
Figure 3. A public example of Google Glass (wearable computer device)1.
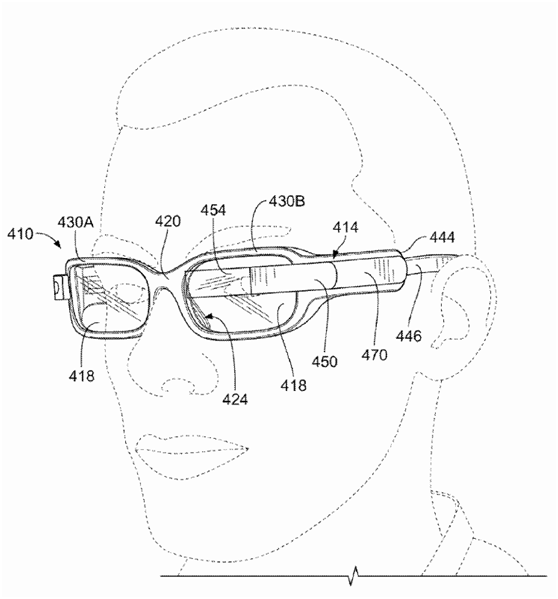
Figure 4. Example 1 of Google Glass is worn by the user.
Figure 5 is two similar structural diagrams of Google Glasses Example 1, in which (a) has one more lens than (b). Style (a) includes an on-board computing system 204 and a camera 206. The display 208 is fixed in the center of a lens, and the computer-generated image can be superimposed on the user's physical vision. The on-board computing system 204 controls the display 208 connected to the waveguide 210 (waveguide 210). Figure 5(b) is another style of Google Glass Example 1. It includes two temples 223, a frame support 224 in the middle, a nose pad 225, an on-board computing system 226, a camera 228, and a temple 223 connected to the glasses. The individual lens elements 230, 230 are placed in front of or close to the user's eyes. The spectacle frames in Figure 5(a) and (b) must be made of plastic or metal with a solid hollow structure, so that the connecting wires and components can be connected inside the glasses.
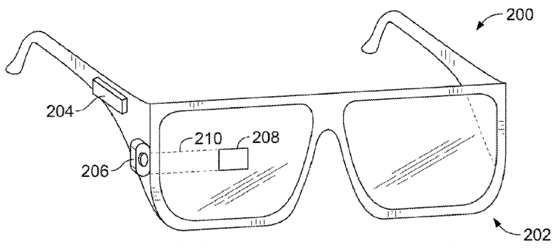
(a)
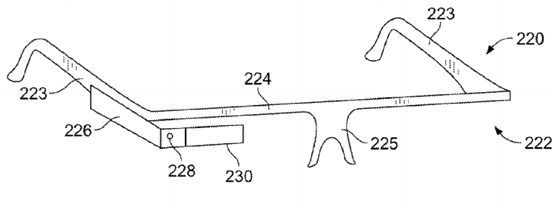
(b)
Figure 5. Two similar structural diagrams of Google Glass Example 1.
Figure 7 shows a schematic diagram of the basis of a computer network, as well as a structural diagram for receiving, transmitting and displaying data. It includes a 310 device, a remote device 330, and a link 320 connecting the two, including wireless links and wired links. Kind of link. This 310 device is used to receive and display information, and is composed of a display system 312 and a memory 318, and is a heads-up display, such as the two example systems shown in FIG. 5. The display system 312 is composed of a processor 314 and a display device 316. The display device 316 can be an optical see-through display or a video see-through display; the processor 314 can receive data from the remote device 330 and use the data with the device 316 display. The processor 314 may be a micro-processor (micro-processor) or a digital signal processor (digital signal processor).
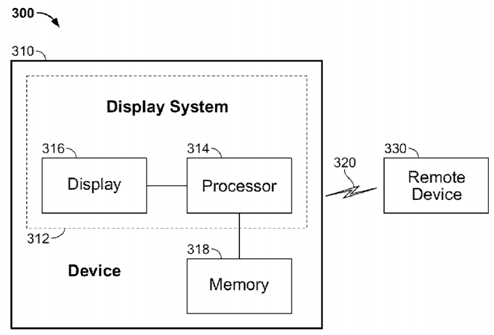
Figure 7. The structure diagram of Google Glass receiving, transmitting and displaying data.
2. Example 2 of Google Glass
Figure 8 is another structural diagram of Google Glasses, which is obviously different from the structural design of Figure 3, and the headband 613 of different sizes is designed to meet the needs of different sizes of head shapes. There is no universality, which may be due to this reason. Google ultimately did not choose this structure. Example 2 of Figure 8 mainly includes earpiece 646 (earpiece 646), arm frame 614, touch input 672, and display 654. The headband 613 can be designed into a more flexible structure to adapt to different head shapes, and elastic materials can be used. Or the headband 613 is made of synthetic material.
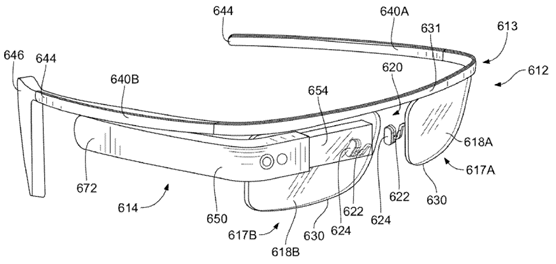
Figure 8. A public example 2 of Google Glass (wearable computer device).
Figure 9 is a detailed display of Figure 8. The arm frame 614 also contains a screw to secure the arm frame to the rail 636. 632 allows the display 654 to be adjusted back and forth so that the display is not close to the user's eyelashes, because Some users have very long eyelashes.
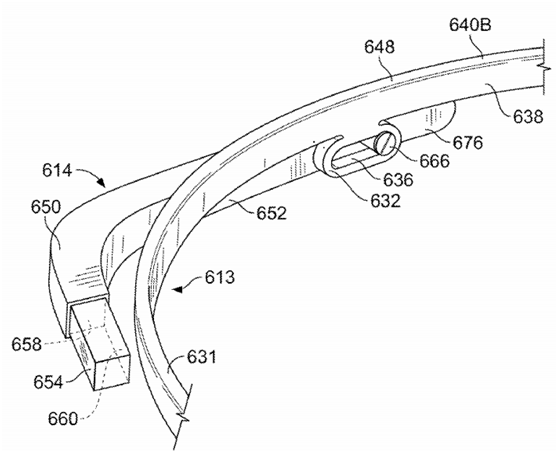
Figure 9. A detailed display of Google Glass Example 2.
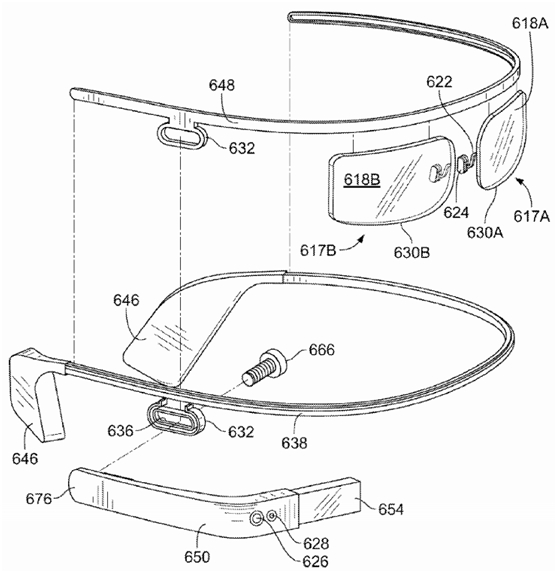
Figure 10. Exploded view of Google Glass example 2.
FIG. 10 is an exploded view of Example 2. It can be seen that the key part of Google Glass is the arm frame 650, which includes a display 654, camera parts 628 and 626, and a touch input 676. Because this patent only shows the original basic model, the input function is relatively small (focus on touch input), but the positioning of Google Glass is an AR system, so the sensor technology must include pupil tracking, voice and image input , But nothing is shown in this patent except for the camera.
According to the hololens patent, it can be regarded as a wearable computer. Its display, input, holographic processor, pupil tracking, and interactive system are all described well, and the weight is relatively heavy. (Hololens2 weighs 566 grams). In contrast, Google Glass is more like a VR system combined with some simple sensors as input. It is because of its simple function that it is so lightweight. Although the positioning of the enterprise version has shifted to enterprise users, the functions still haven't made great progress.
